Categories
Social and governance indicators
Social Indicators
In this category, you can track common indicators related to diversity, labor, and philanthropy for the purpose of reporting your performance to stakeholders. The category primarily serves as a central repository, though the occupational safety section also outputs various incident rates.
The Social category can be accessed under Measure. There are six subcategories that can be tracked:
-
Diversity of governance bodies
-
Diversity of employees
-
Training and education
-
Collective bargaining
-
Occupational safety
-
Volunteering and donations
Cadence for tracking
-
You can track these metrics at a location level or at a cCompanywide level
-
You can track these metrics month over month (or as needed) or once a year. If you decide to track once a year, simply put all your information for a category into a single month. We recommend putting this information into December of the reporting year.
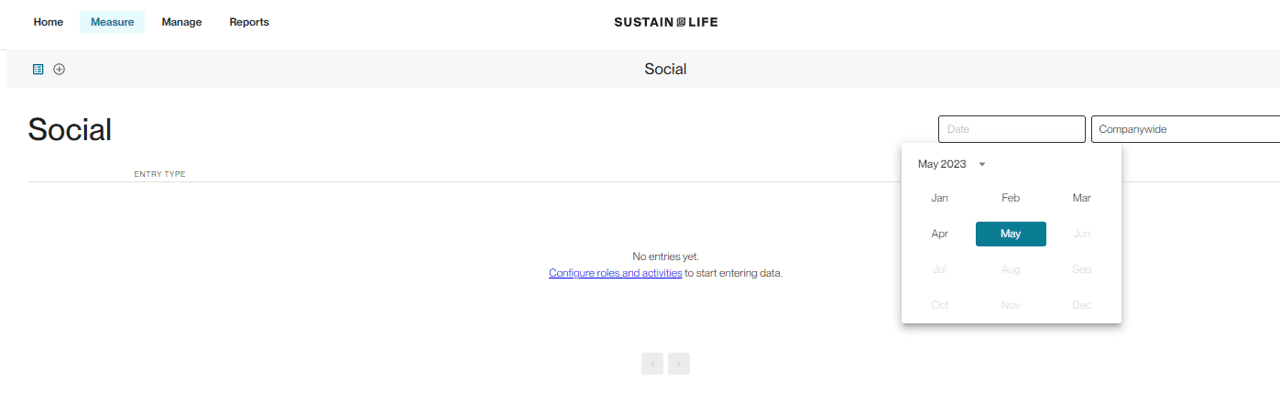
Begin by selecting the date and location. Click on the Configure roles and activities link to set up your data entry forms.
Next, select the first indicator you want to track. You can also toggle off indicators you don’t plan to track.
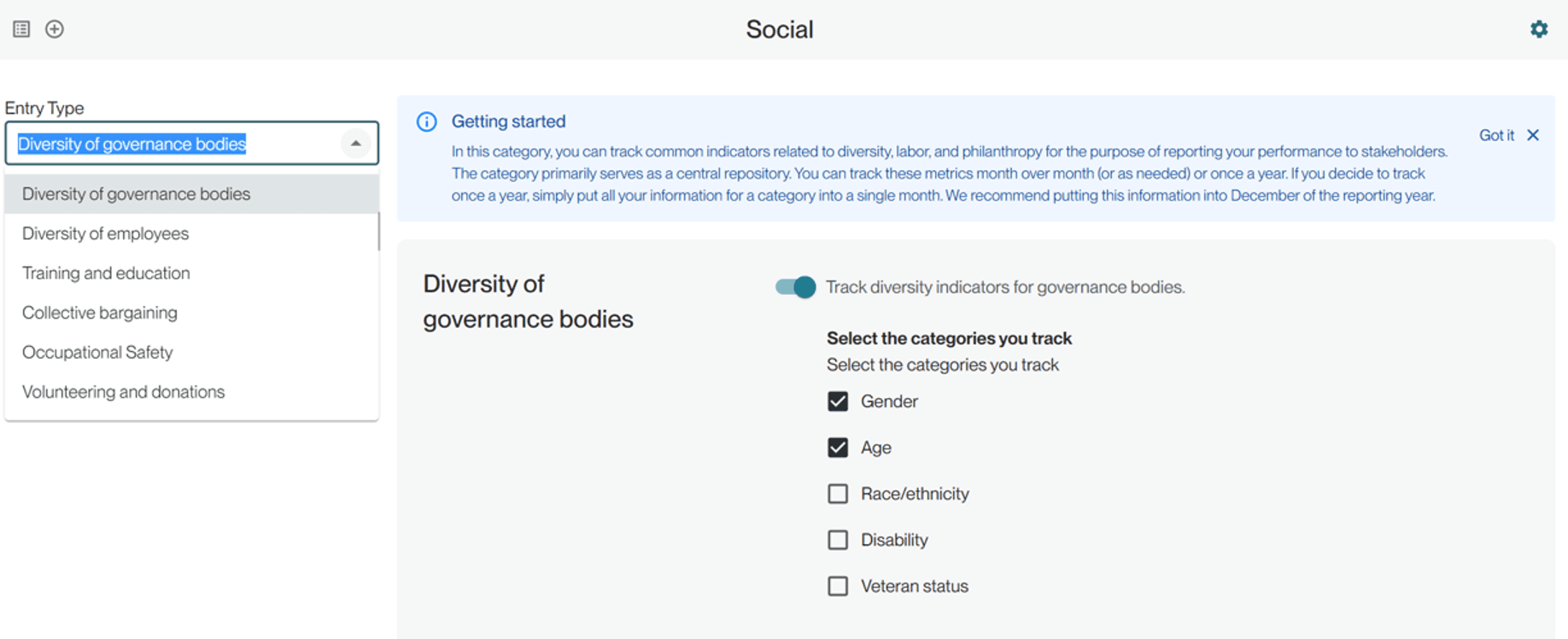
Before you can begin tracking, you need to complete your configurations. We first ask you to select the categories you currently track as diversity indicators for governance bodies.
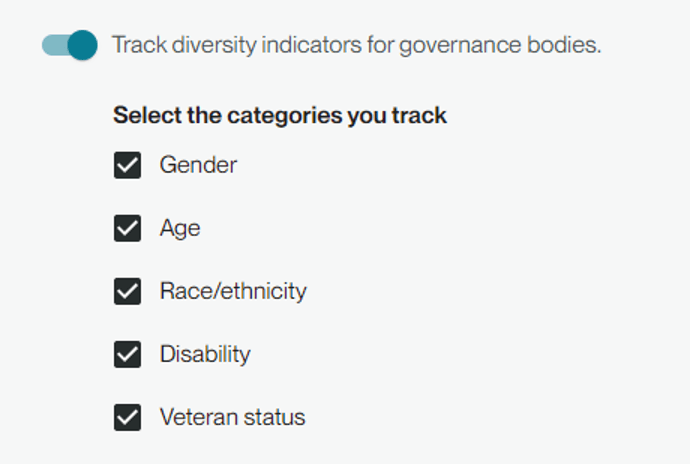
In case you are missing information, for example because employees opted out of self-identification, there is an Unknown option for each category.
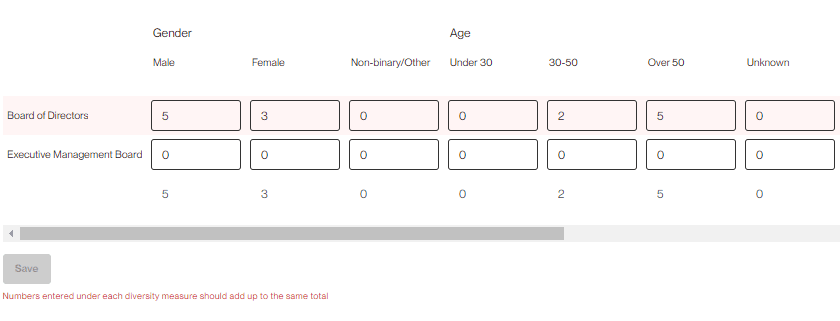
After you have indicated what categories you track, we ask you to create labels for your company’s governance bodies (e.g., leadership board, board of directors, etc.). These are completely customizable and should match your internal HR structure.

Once you have named your governance bodies, you can save in the bottom right and fill out the table that appears on the manual entry page.
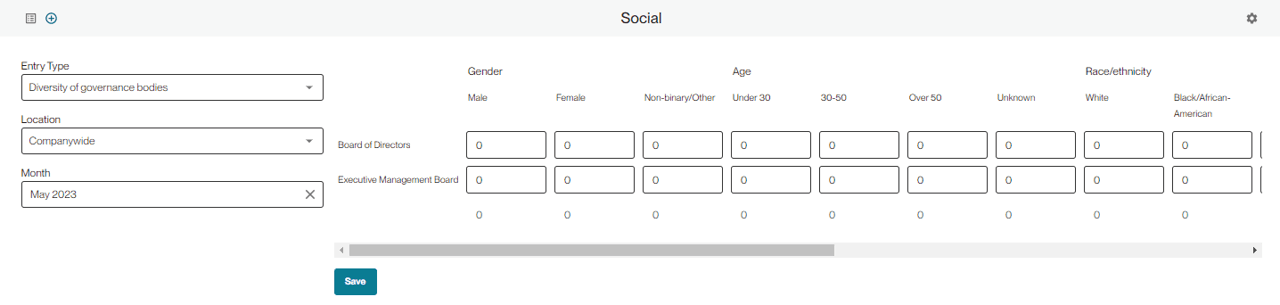
Your totals will sum on the bottom of each column. Once you are finished inputting your data press save.
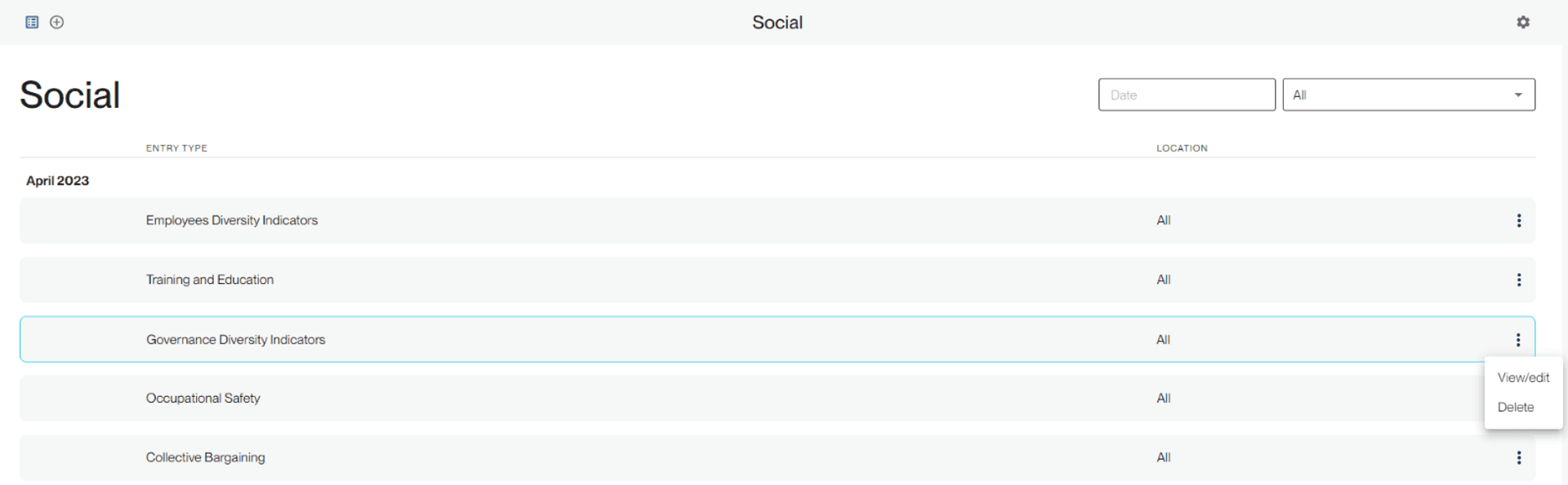
Your entry will be saved in the ledger, and you can view, edit or delete it at any point.
In the entry type drop down, you can select Diversity of employees. You are again able to select diversity indicators that you track. You can also input labels for all your company’s employee categories, following your internal naming conventions and organizational structure.
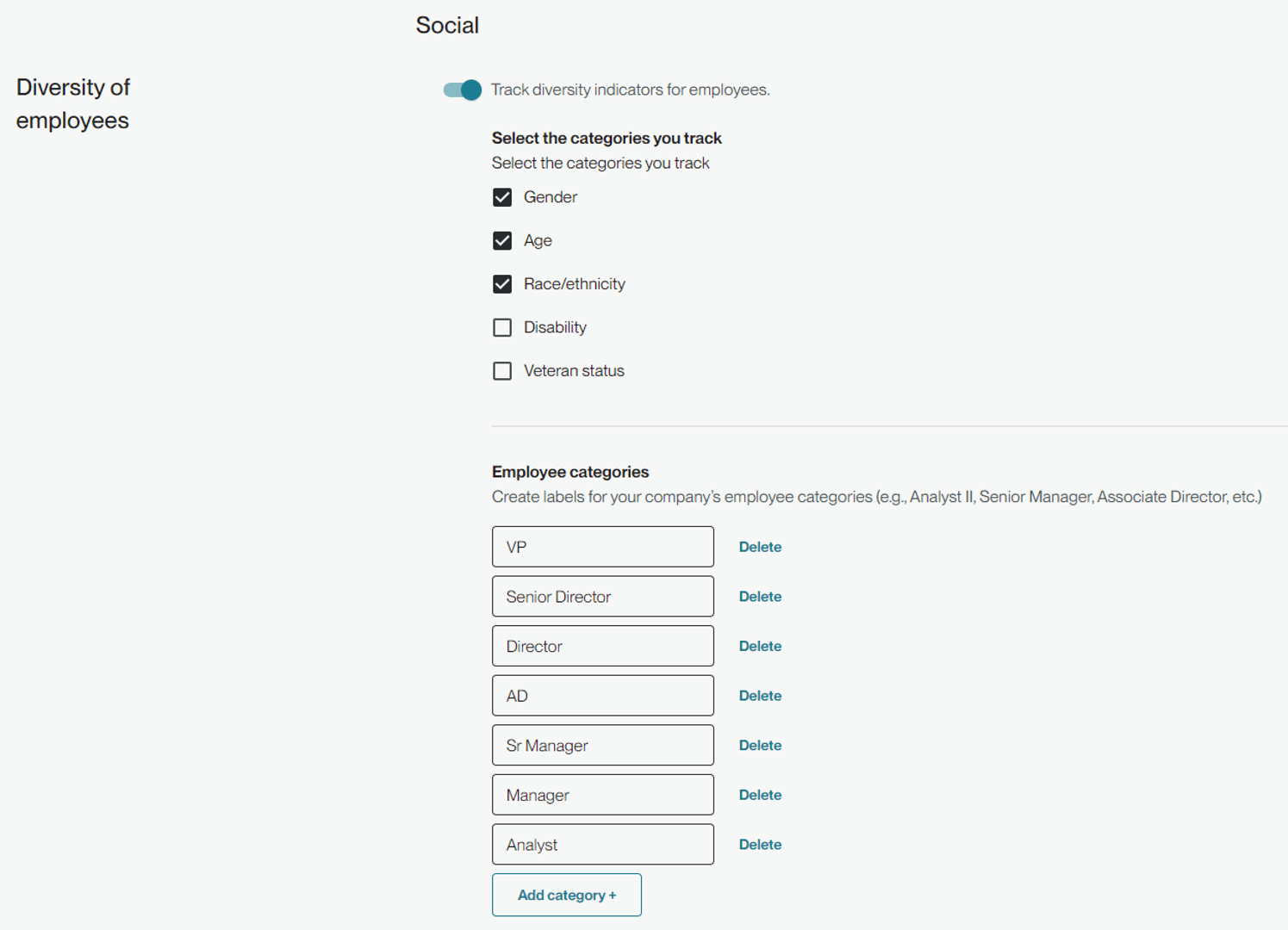
Much like Diversity of governance bodies, your totals must be equal in each bucket. You can also track by location or companywide.
From the configurations page you can select what indicators you want to track for participants.
Gender will break out training hours into Male, Female, Non-binary/other and Unknown for when you are not able to track that information for everyone.
The other indicator you can track is training hours by employee category.
The bottom section is where you can input the names of the training subjects that you ask your employees to complete. You can input companywide and/or location level training items. You should label training with the same names that you use internally. Like other sections in social, these can be tracked once a year or throughout the year.
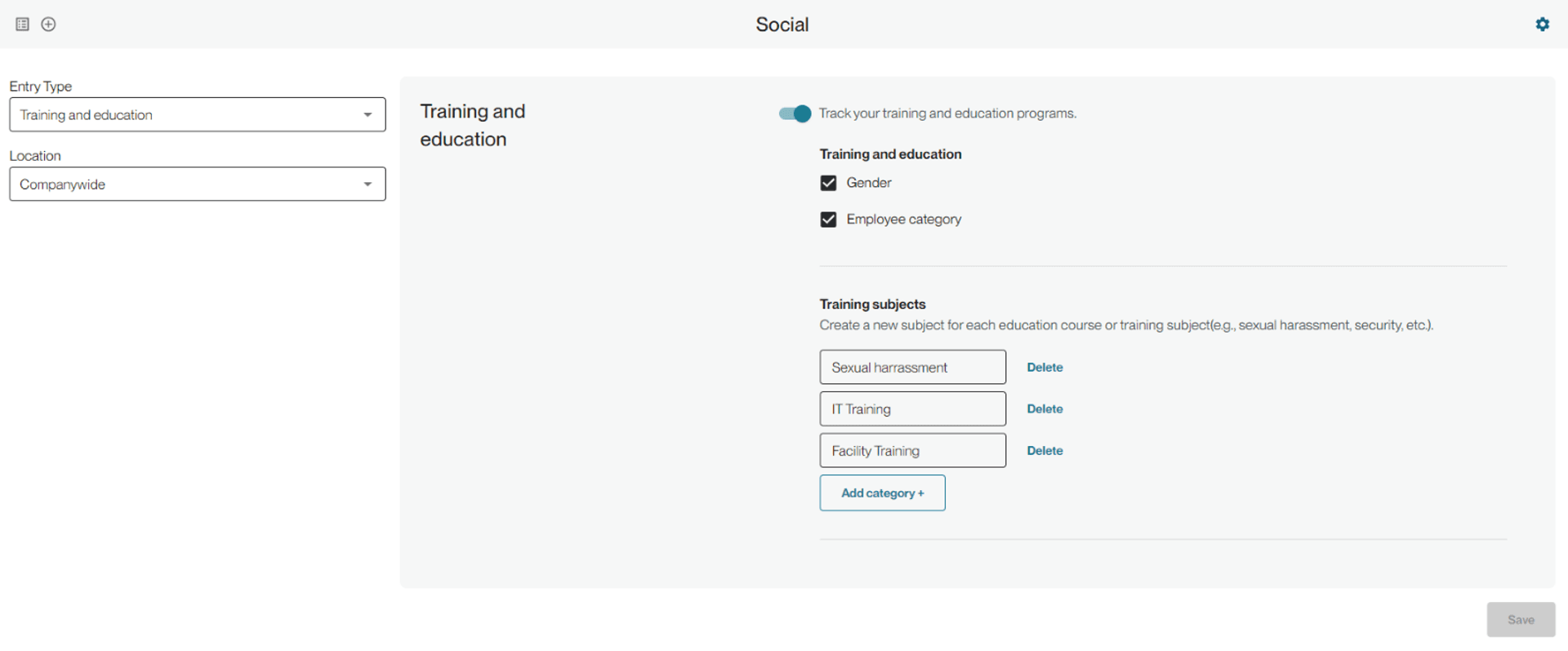
Whatever you select in the configurations will appear in the manual entry table. Additionally, you can track training hours for each training item as well. This column will appear at the beginning of the table.
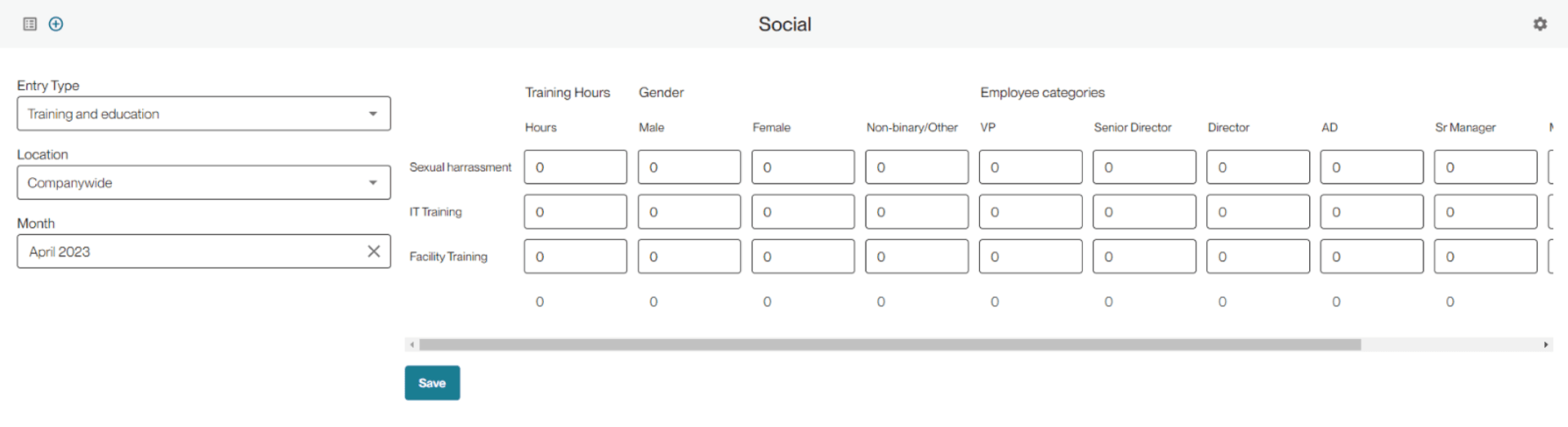 If you’re tracking by gender and employee category, note that the number of training hours for each must sum to the same value. Then enter that same total into the Hours column to where total hours = sum of hours by gender = sum of hours by employee category.
If you’re tracking by gender and employee category, note that the number of training hours for each must sum to the same value. Then enter that same total into the Hours column to where total hours = sum of hours by gender = sum of hours by employee category.
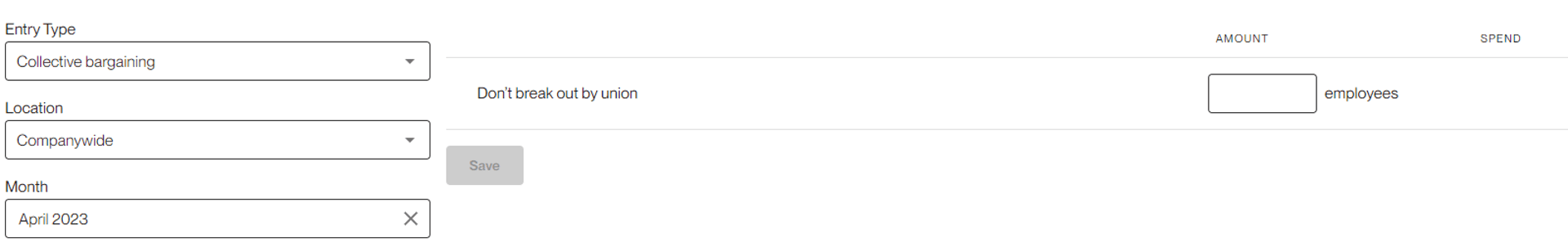
The collective bargaining section allows you to track union membership. If you’re unable to break out employees by union, you can track a company total by selecting “Don’t break out by union.”
Union membership can be challenging to track, as employees don’t have to disclose when they join a union. In the EU, union membership fees are sometimes paid from wages, in which case the name of the union and the employee count are available. Some companies use national statistics to estimate union membership. The purpose of tracking union membership is to report to stakeholders that your company honors your employees’ right to join unions and bargain collectively.

If “Don’t break out by union is selected, the manual entry requires a single company total of union members.
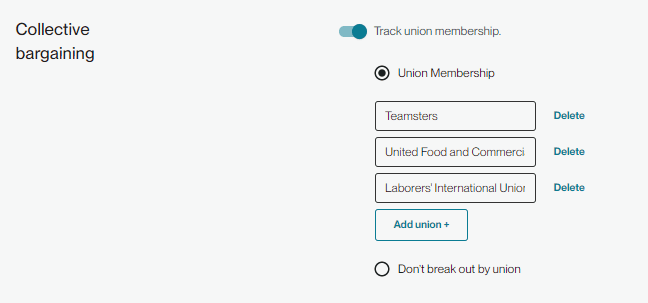
If you do have membership information for individual unions, you can add the names to the configuration page at a companywide or location level.
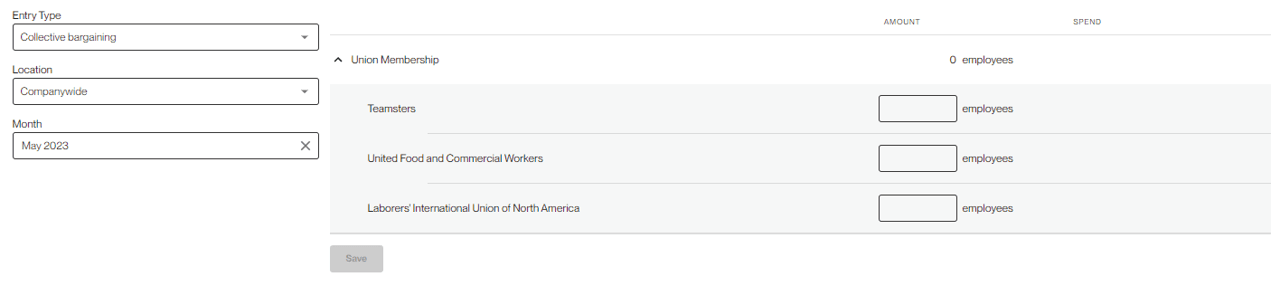
You can then add employee counts to each of the unions you have added.
The occupational safety section is not a comprehensive tracking or incident management system but meant to capture commonly reported disclosures in sustainability reporting. On the configuration page, select what your company tracks and if you want to track those metrics companywide or at a location level. You can track lost days, near misses, five common types of incidents, and hours worked broken out by permanent and temporary employees.
Hours worked, lost workdays, and number of incidents are used to calculate standard safety incident rates, including the following:
-
Recordable incident rate (IR)
-
Incident rates from days away, restrictions and job transfers (DART)
-
Lost time incident rate (LTIR)
-
High-consequence incident rate
-
Lost workday rate (LWR)
-
Annual fatality rate
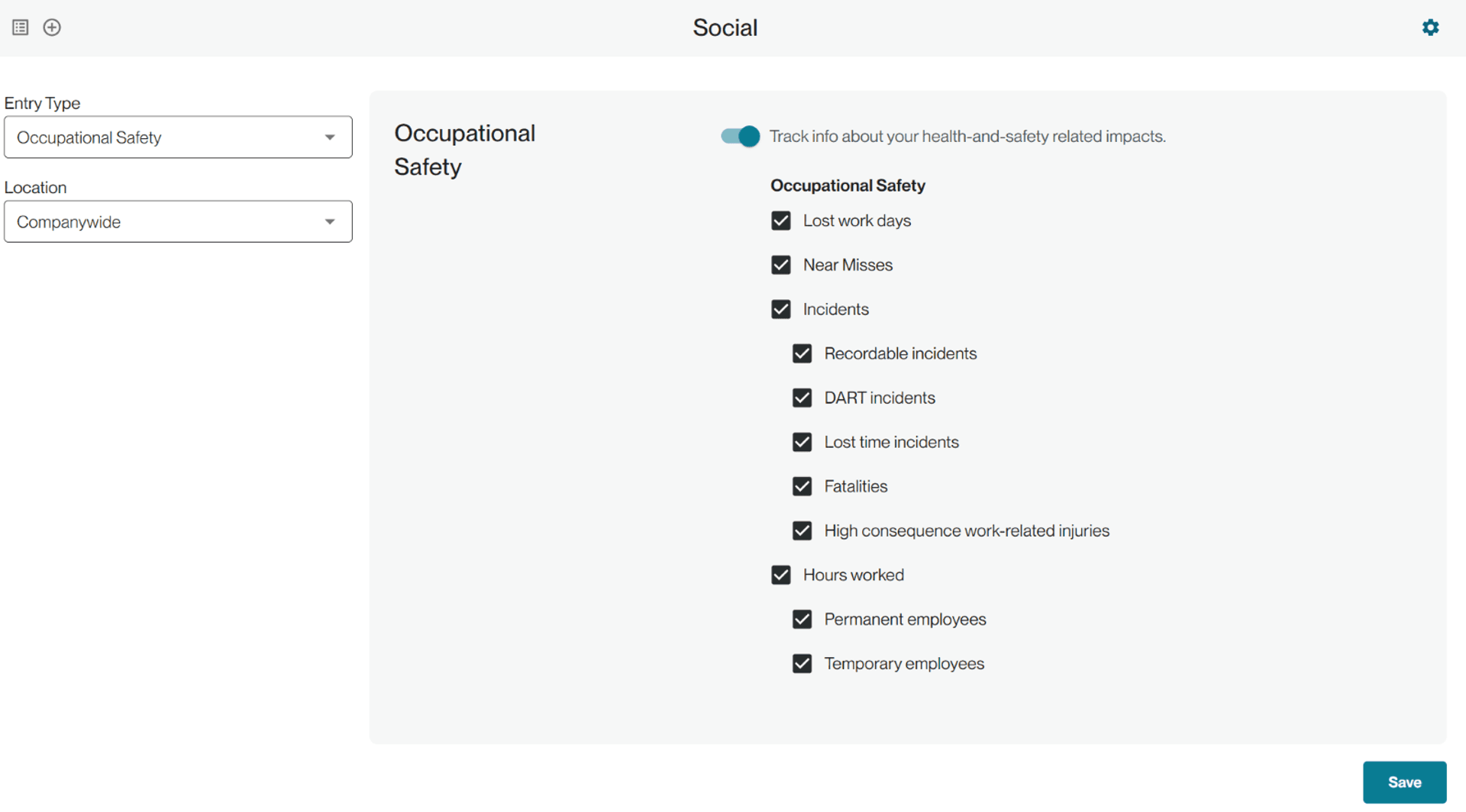
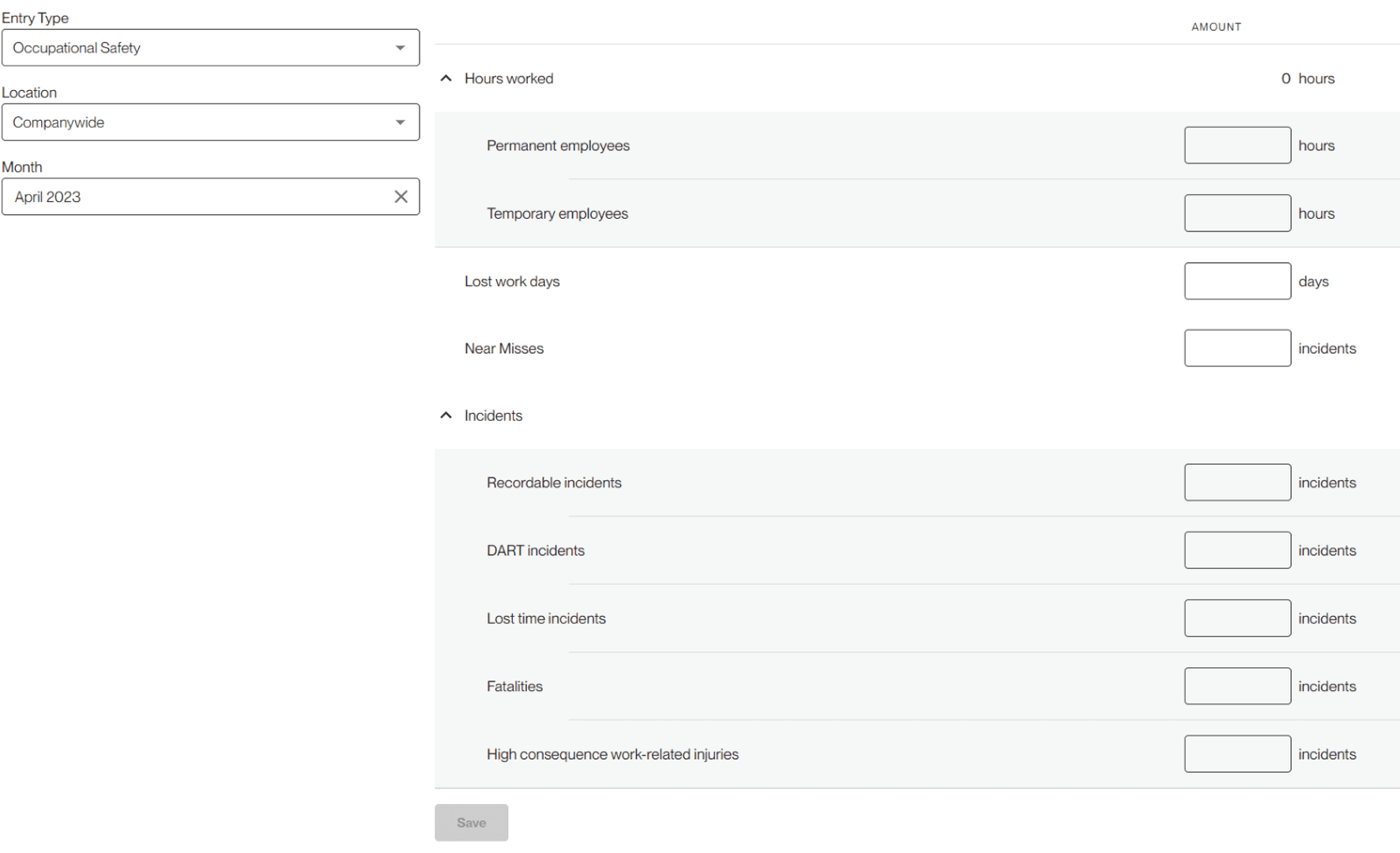
Hours worked is tracked in hours, lost workdays in days, and the rest are tracked as number of incidents/near misses.
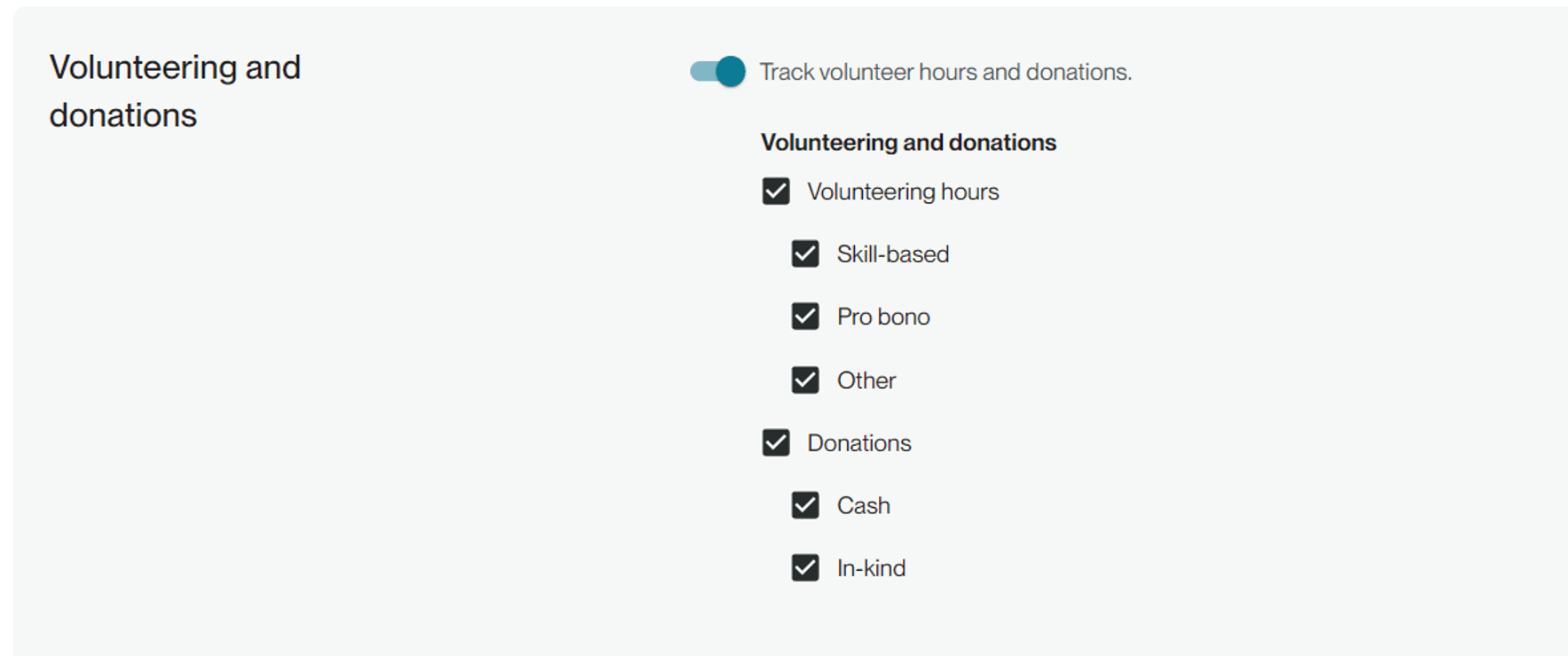
This is where you track volunteer hours and donations. On the configuration page, select all applicable types. They will then appear on the manual data entry screen.
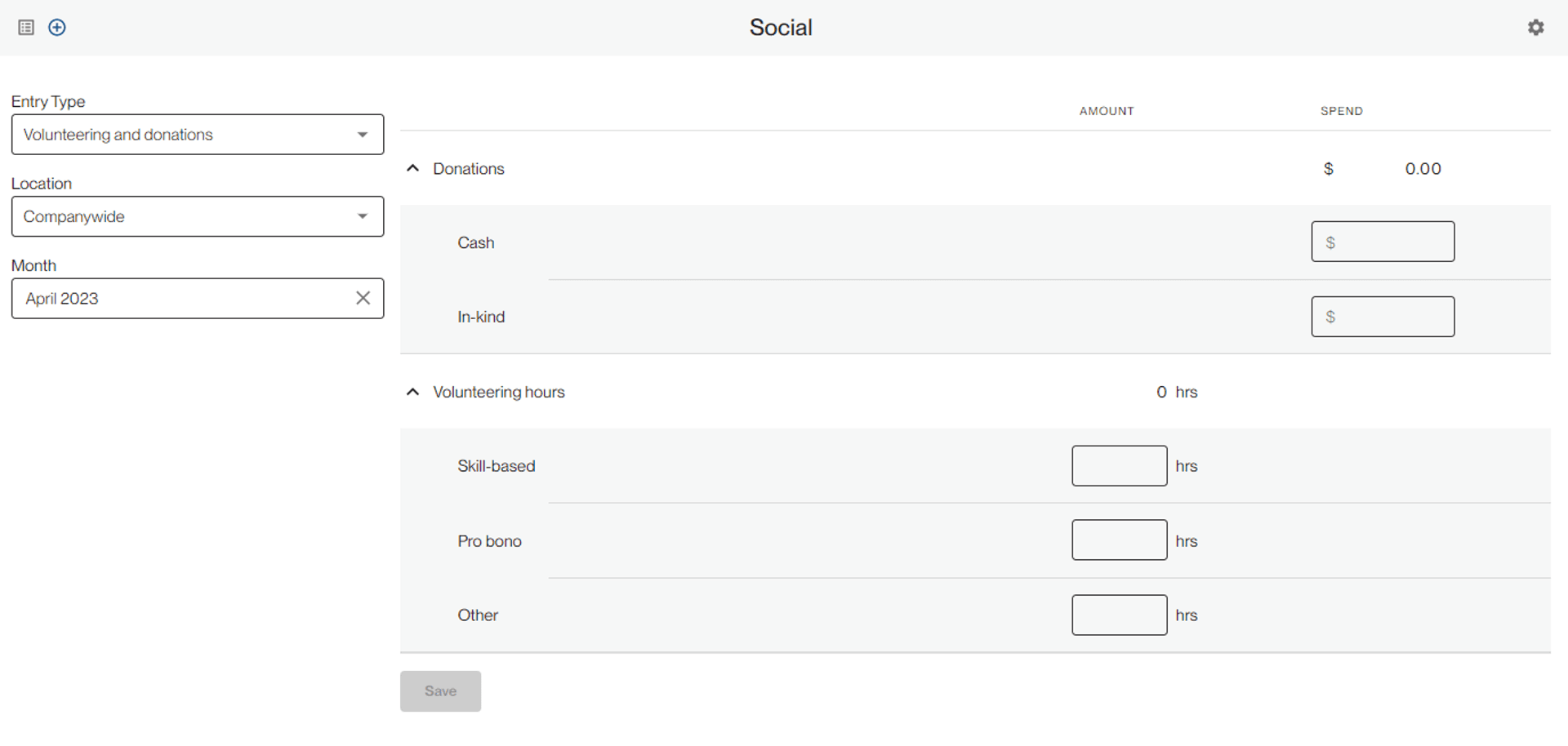
Cash and In-kind donations are tracked by spend (if estimating the value of in-kind donations, consult with your tax team to find the best approach), and volunteer hours are by count. You can track this at any interval, including monthly, quarterly or annually. If quarterly, we recommend documenting it in the last month of the quarter. If annually, we recommend entering it for December. Consistency will make your internal data audits easier.
Under the Governance cateogry you will find Fines and sanctions. Please only record confirmed incidents, so don't include pending or under investigation cases in this section. This category is used for for compliance breaches across all areas of your company, not just areas specific to sustainability.
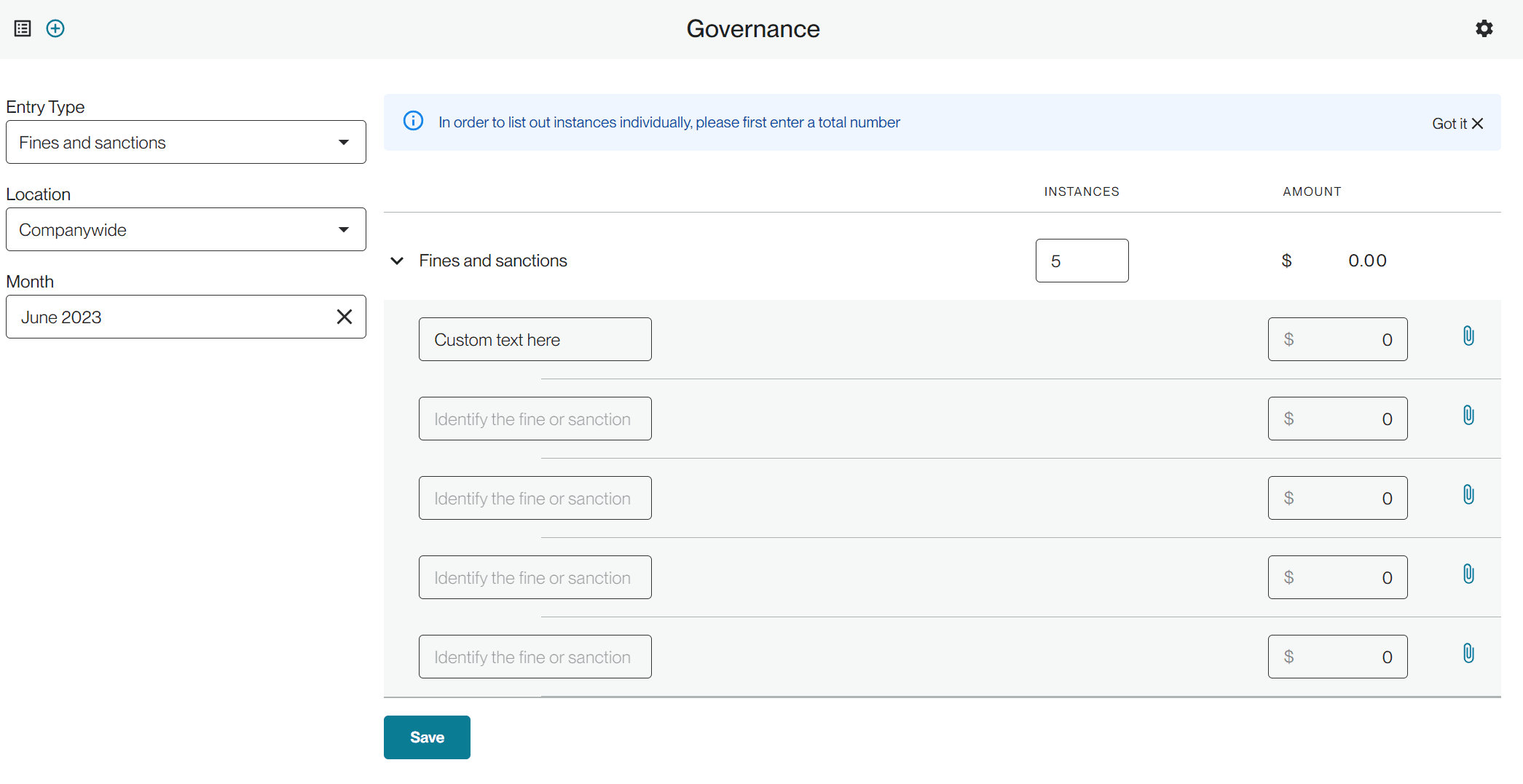
On the configuration page, select if you are simply tracking the total number of instances or if you want to track each individually.
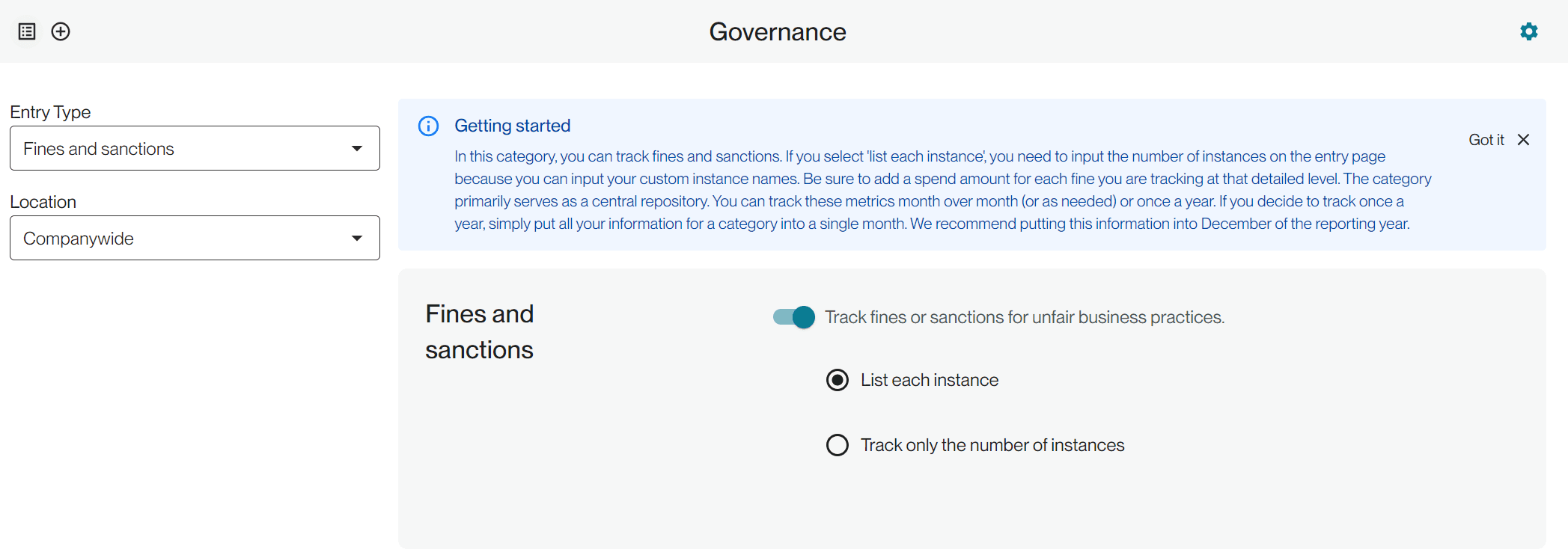
If you track only the number of instances, we will simply allow you to input the number of fines/sanctions for a given time period and a dollar amount if desired.
If you select "list each instance", the input form will appear with an instance count at the top. Start by inputting a number and the appropriate amount of rows will appear underneath. You can add a title/name for each of the fines or sanctions that you are tracking, as well as a spend amount.
- Collective bargaining: The process of negotiating terms of employment between employees, usually represented by a worker’s union, and their employer.
Occupational safety
- Near miss: A narrowly avoided incident. Near misses are commonly tracked in safety management programs as a means of identifying weaknesses that could lead to accidents. Example: An employee walks past a tall stack of boxes. The stack collapses due to poor stacking and the employee is almost struck by one of the boxes. The safety team can now take measures to improve stacking before an accident happens.
- Recordable incidents: A recordable incident is a work-related injury or illness that results in any of the below. Note that this is U.S. Occupational Health and Safety Administration terminology, which may differ in other jurisdictions.
- Work-related fatality
- Work-related injury or illness that results in loss of consciousness, days away from work, restricted work, or transfer to another job
- Work-related injury or illness requiring medical treatment beyond first aid
- Work-related diagnosed case of cancer, chronic irreversible diseases, fractured or cracked bones or teeth, and punctured eardrums.
- There are also special recording criteria for work-related cases involving: needlesticks and sharps injuries; medical removal; hearing loss; and tuberculosis.
- DART incidents: Work-related incidents involving lost workdays (“days away”), work restrictions or job transfer
- Lost time incidents: Work-related incidents resulting in time away from work (beyond the day of the injury)
- High consequence work-related injuries: Injuries from which workers can’t recover (e.g., amputation, loss of sight) and injuries with full recovery time exceeding six months (e.g., complex fracture, some ergonomic injuries)
Volunteering and donations
- Pro bono: Provision of professional services at a low or no cost, including legal support, accounting, consulting, tax preparation, etc.
- Skill-based: Skilled volunteer work applies professional skills, e.g., mentoring, teaching people how to use specific software, repairing a building, etc.
- In-kind: Refers to non-monetary charitable donations, e.g., furniture, clothing, equipment, food, supplies, etc.
What is the benefit of tracking these high-level data points here, when we already have them in other internal systems?
There are two primary benefits:
-
Having a centralized place that holds all your sustainability reporting data. This is especially helpful if you need to quickly access information for previous years to double-check data or develop year-over-year comparisons.
-
Getting the data into the right format. For instance, if your HRIS lead and your safety lead are required to provide data and have access to the application, they can see in which format to enter data to help get it report-ready. And if someone new joins the team, they can easily match the format each year.
Where can I find this type of information?
For diversity of governance bodies, you may need to reach out to your legal team. Sometimes, an individual board member will be able to provide an educated guess for age range and race, but keep in mind that guessing could miss distinctions in gender and ethnicity. You can also talk to HR to see if they’re willing to tackle board member self-identification.
Employee diversity can be provided by HR and is usually housed in an HR information system (HRIS). Ask the team to set up a report or have someone go directly into the app to enter data for a specific interval. The data itself tends to come from voluntary self-identification questionnaires provided during the job application process. In the U.S., these questionnaires usually ask for race/ethnicity, but in the EU, employers cannot ask for this information. Some employers periodically administer voluntary, anonymous diversity surveys. These can ask for anything from religious and political affiliation to gender identity and help companies better understand their workforce.
If your company has a learning & development function or training manager, they can provide training data. Be sure to speak with them early, as training hours are often not tracked by gender or employee category. If there’s no dedicated training department, consult your HR team.
Collective bargaining information is also normally managed by HR, but keep in mind that many companies can’t track union membership reliably.
Safety data is managed by occupational health and safety personnel (HSE, EHS, etc.), normally at the facility level before being aggregated at the company level. They’ll likely have a comprehensive process for tracking, managing, and reporting safety incidents. If they’re already tracking and calculating incidents and incident rates in a separate platform, determine if it makes sense to settle on one platform or duplicate the information in two systems.
Volunteer hours are tracked by various teams across companies and company locations, such as philanthropic committees, community teams, event ambassadors, green teams, or HR. You can save time by providing team members who have access to this information at each facility with login information to enter volunteer hours directly. Donations tend to be tracked by finance teams. It generally makes sense to request this information just once for the full year.
What’s the difference between skill-based and pro-bono volunteering?
Pro-bono volunteer work provides professional services at a low or no cost, including legal support, accounting, consulting, tax preparation, etc. These services are usually charged at a high hourly rate. Skilled volunteer work applies professional skills, e.g., mentoring, teaching people how to use specific software, repairing a building, etc.
Can we do an integration, flat file transfer or bulk upload to get hours worked data into the app?
At this time, the app only accepts manual entries for social indicators.
Some of these indicators seem selective. How did you determine which to offer for tracking?
We prioritized indicators that are commonly tracked across sustainability reporting standards and ESG disclosure systems, but plan to add others in the future to align even further.
Our own calculated safety incident rates don’t match the ones you’ve calculated. Which formulas did you use?
We provide separate outputs for permanent and temporary employees. Our calculations use the 200,000 value. While this calculation method is common and aligns with OSHA reporting requirements in the U.S., we recognize that there are other ways to calculate these rates (e.g., using 1,000,000) and that some jurisdictions have specific requirements with which we may not align.
Our incident rate formula multiplies the number of incidents in a specified period by 200,000 and divides the result by hours worked during the same period. We also provide rolling rates, using the aggregate number of incidents over time.
Copyright 2025 Sustain.Life All rights reserved